CKA를 준비하면서 공부한 요약 내용입니다.
Design a k8s cluster
Purpose
- Education
- Minikube
- Single node cluster w\ kubeadm/GCP/A
- Development & Testing
- Multi-node cluster with a single master and multiple workers
- setup using kbeadm tool or quick provision on GCP or AWS or AKS
- Hosting Production Applications
Hosting Production Applications
- High Availability Multi node cluster with multiple master nodes
- kubeadm or GCP or Kops on AWS or other supported platforms
- Upto 5000 nodes
- Upto 150,000 PODs in the cluster
- Upto 300,000 Total Containers
- Upto 100 PODs per Node
Cloud or OnPrem
- Use Kubeadm for on-prem
- GKE for GCP
- Kops for AWS
- AKS for Azure
Storage
- High Performance - SSD Backed Storage
- Multiple Concurrent connections - Network based storage
- Persistent shared volumes for shared access across multiple PODs
- Label nodes with specific disk types
- Use Node Selectors to assign applications to nodes with specific disk types
Nodes
- Virtual or Physical Machines
- Minimum of 4 Node cluster
- Master vs Worker Nodes
- Linux X86_64 Architecture
- Master nodes can host worloads
- Best practice is to not host workloads on Master nodes
ETCD in HA
ETCD
- a distributed reliable key-value store that is Simple, Secure & Fast
Key-value store
- Tablular/Relational Databases
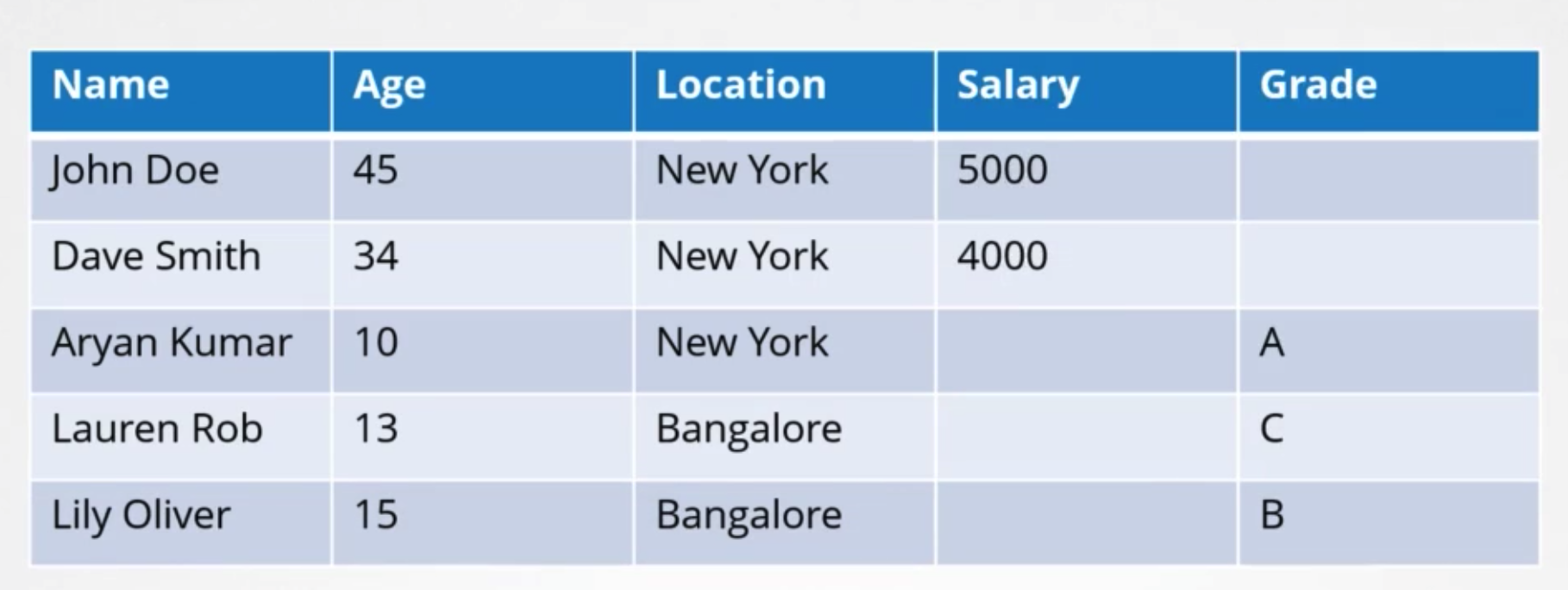
- key-value store

Distributed
- it is possible to have your database across multiple servers
Consistent
- how does it ensure the data on all the nodes are consitent?
- ETCD ensures that the same consistent copy of the data is available on all instances at the same time
- how does do that?
- read ← easy
- write
- two write request coming
- only one of the instances is responsible for processing the writes
- interanally the other nodes elect a leader among them.
- one node: leader
- other nodes: followers
- leader process write
- leader makes sure that the other nodes are sent a copy of the data
- if the writes come in through any of the other follower nodes, then they forward the wirtes to the leader internally
Leader Election - RAFT
- How to elect leader in ETCD
- → use RAFT protocol
방법
- use RAFT Algorithm
- random timers for initiating requets
- first nodes sent out a requetst to the otehr node requesting permission to be the leader
- other managers receiving the request responds with their vote and node assumens the leader role
- leader is elected, it sends out notifications at regular intervals to other masters informing them that it is continuing to assume the roloe of the leader
- other nodes do not receive a notifications from the leader at some point time
- nodes initiate a re-election process among themselves
- new leader is identified