- 업데이트 내역:
- 2021.07.16 Brier Score 수식 추가
TL;DR
MLOps를 성공적으로 수행하기 위해서는 아래와 같은 상황들이 일어나지 않도록 해야 합니다.
- 데이터 유출에 의해 과도하게 최적화(overly optimistic)된 모델이 배포된 상황
- 모델이 배포된 후 아무런 관리없이 계속해서 사용 되는 상황
- Hyper-parameter Optimization이 이루어지지 않는 상황
- 실제로 성능이 검증되지 않는 기법이 파이프라인에 바로 적용되는 상황
- 모델 성능 향상의 요인을 정확히 파악할 수 없는 상황
- Test 데이터가 독립적이지 못한 상황
- Concept drift에 대응할 수 없는 상황
- 잘 보정되지 않은 모델을 배포함으로서 머신러닝 파이프라인 전체의 신뢰도 하락이 일어나는 상황
- 모델을 개발하는 과정에서 데이터가 수정되는 과정이 기록되지 않는 상황
해당 포스트는 Using AntiPatterns to avoid MLOps Mistakes를 읽고 요약한 내용입니다.
원문이 더 자연스럽게 이해되는 경우에는 따로 번역하지 않고 원문 그대로를 담았습니다.
AntiPatterns
Anti Pattern 이란?
AntiPatterns provide real-world experience in recognizing recurring problems in the software industry and provide a detailed remedy for the most common predicaments. AntiPatterns highlight the most common problems that face the software industry and provide the tools to enable you to recognize these problems and to determine their underlying causes.
출처: https://sourcemaking.com/antipatterns
MLOps를 개발 및 배포할 때 발생할 수 있는 문제들
- Does the data processing pipeline have unintended side effects on modeling due to data leakage or HARKing?
- What happens when models ‘misbehave’ in production? How is this misbehavior measured? Are there compensatory or remedial pipelines?
- How often are models re-trained and what is the process necessary to tune models? Is the training and model tuning reproducible?
- How is model performance assessed and tracked to ensure compliance with performance requirements?
- What constitutes a material change in the MLOps pipeline? How are changes handled?
- Where does the input data reside and how is it prepared on a regular basis for input to an ML model?
Types of AntiPatterns
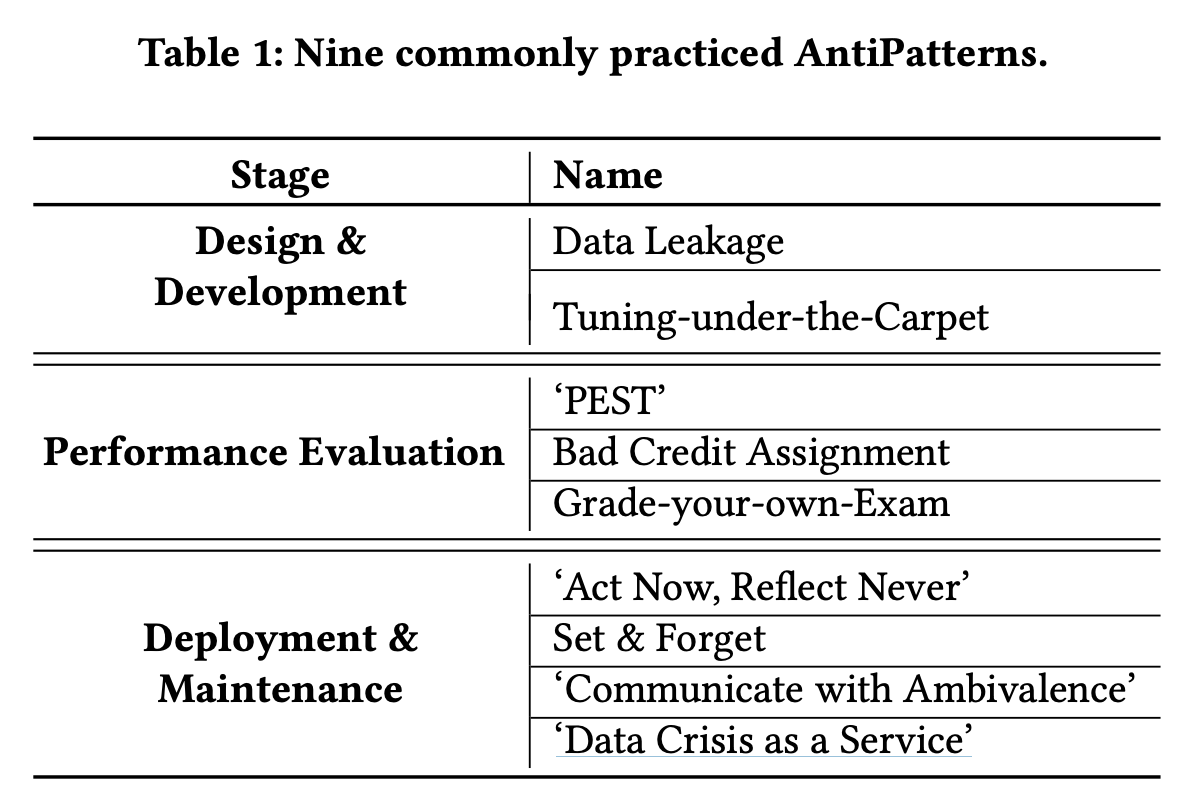
Production 단계에서는 모델들은 다음과 같은 패턴으로 계속해서 바뀌게 됩니다.
- replaced by a newer (e.g., more accurate) model
- retrained with more recent data 2.1) with keeping existing hyper-parameters or ranges constant or fixed 2.2) with new search for hyper-parameters
모델이 바뀌는 과정에서 여러가지 AntiPattern들을 마주하게 되는데 논문에서는 다음과 같은 9개의 상황을 제시합니다.
- Data Leakage AntiPattern
- ‘Act Now, Reflect Never’ AntiPattern
- Tuning-under-the-Carpet AntiPattern
- ‘PEST’ AntiPattern
- Bad Credit Assignment AntiPattern
- Grade-your-own-Exam AntiPattern
- Set&Forget AntiPattern
- ‘Communicate with Ambivalence’ AntiPattern
- ‘Data Crisis as a Service’ AntiPattern
1. Data Leakage AntiPattern
데이터 유출에 의해 과도하게 최적화(overly optimistic)된 모델이 배포된 상황입니다.
Data leakage란 직역하면 데이터 유출이라는 뜻입니다. Data leakage가 된 데이터로 모델을 학습한다면 모델이 과도하게 최적화가 됩니다. 과도하게 최적화된 모델을 배포할 경우 모델 성능의 하락으로 인한 문제가 발생할 수 있습니다. 일반적으로 데이터는 Row와 Column으로 이루어져 있는데 양 방향에서 데이터 유출이 생길 수 있습니다
- Feature Leakage (Column-wise leakage)
- caused by a duplicate label, a proxy for the label, or the label itself
- For example, including a “MonthlySalary” column when predicting “YearlySalary”
- Training Example Leakage (Row-wise leakage)
- caused by improper sharing of information between rows of data.
- For example, suppose a model is developed to predict an individual’s risk for being diagnosed with a particular disease within the next year.
출처: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leakage_(machine_learning)
논문에서는 이러한 데이터 유출의 상황 4가지를 제시합니다.
- Peek-a-Boo AntiPattern
시계열 데이터의 경우 실제 발생 시간과 측정 시간의 차이(lag)가 있을 수 있습니다. 그런데 이러한 시계열 데이터를 여러 소스에서 받고 이를 한 데이터셋으로 만든 후 모델을 학습한다면 각 데이터의 lag들이 문제가 될 수 있습니다. - Temporal Leakage AntiPattern
예측 문제에서 데이터를 train, test 을 sequential하게 나누지 않을 경우 독립이어야 하는 두 데이터가 높은 상관관계를 가질 수 있습니다. - Oversampling Leakage AntiPattern
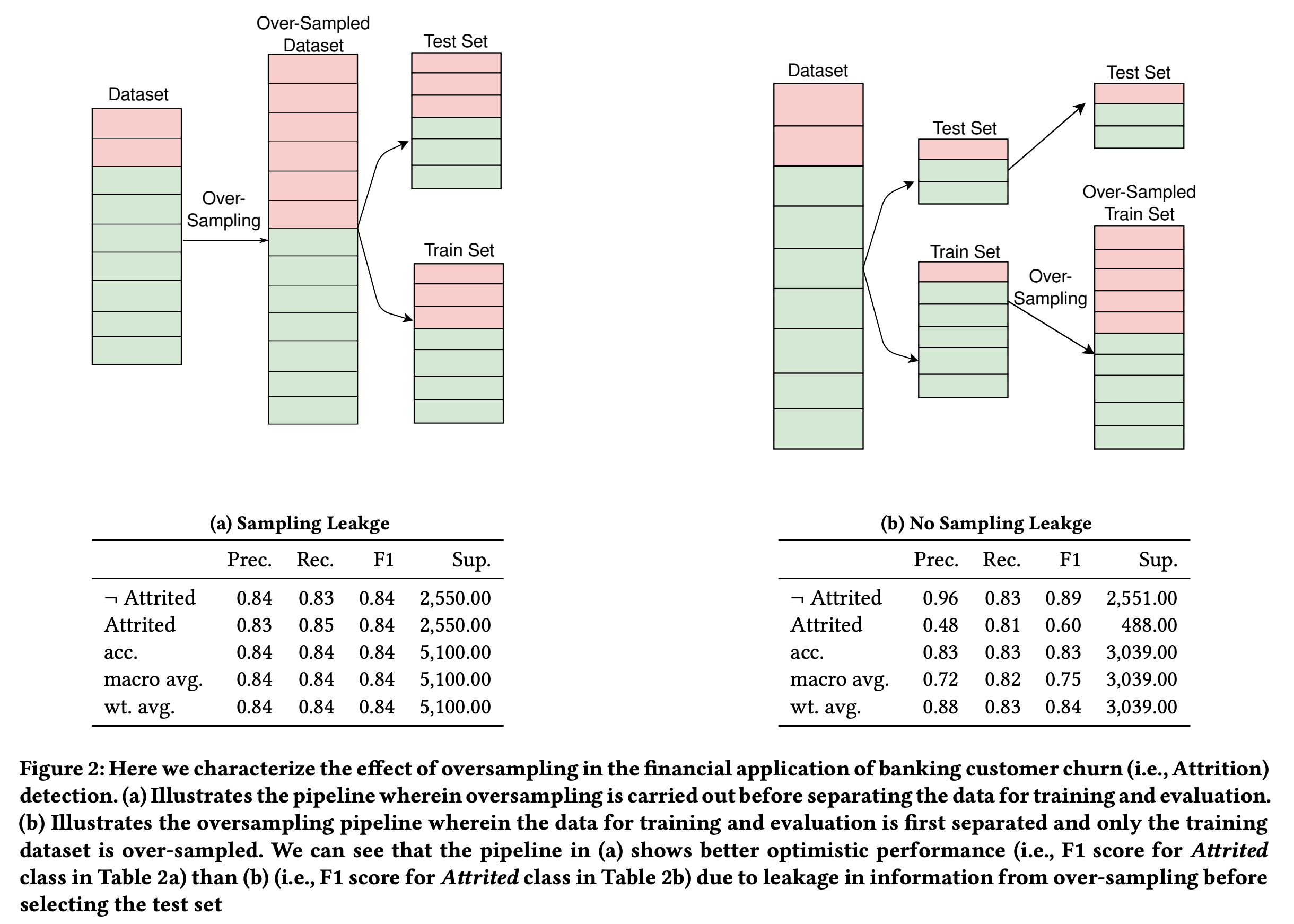 Oversampling을 상황에서도 데이터 유출이 일어날 수 있습니다. SMOTE와 같은 oversampling 기법은 tarin, test 가 이미 구분된 뒤에 실행되어야 합니다. 그런데 이러한 구분 전에 oversampling을 실행한다면 정보 유출의 가능성이 생깁니다.
Oversampling을 상황에서도 데이터 유출이 일어날 수 있습니다. SMOTE와 같은 oversampling 기법은 tarin, test 가 이미 구분된 뒤에 실행되어야 합니다. 그런데 이러한 구분 전에 oversampling을 실행한다면 정보 유출의 가능성이 생깁니다. - Metrics-from-Beyond AntiPattern
이 패턴은 pre-processing leakage, hyper-parameter leakage 에서 볼 수 있습니다. 예를 들어서 전처리를 진행할 때 train 과 test를 묶어서 진행하는 경우입니다.
2. ‘Act Now, Reflect Never’ AntiPattern
모델이 배포된 후 아무런 관리없이 계속해서 사용 되는 상황입니다. 이러한 상황에서는 다음과 같은 문제들에 대처할 수 없게 됩니다.
- Concept drift
- Irrelevant or easily recognisable erroneous predictions
- Adversarial attacks
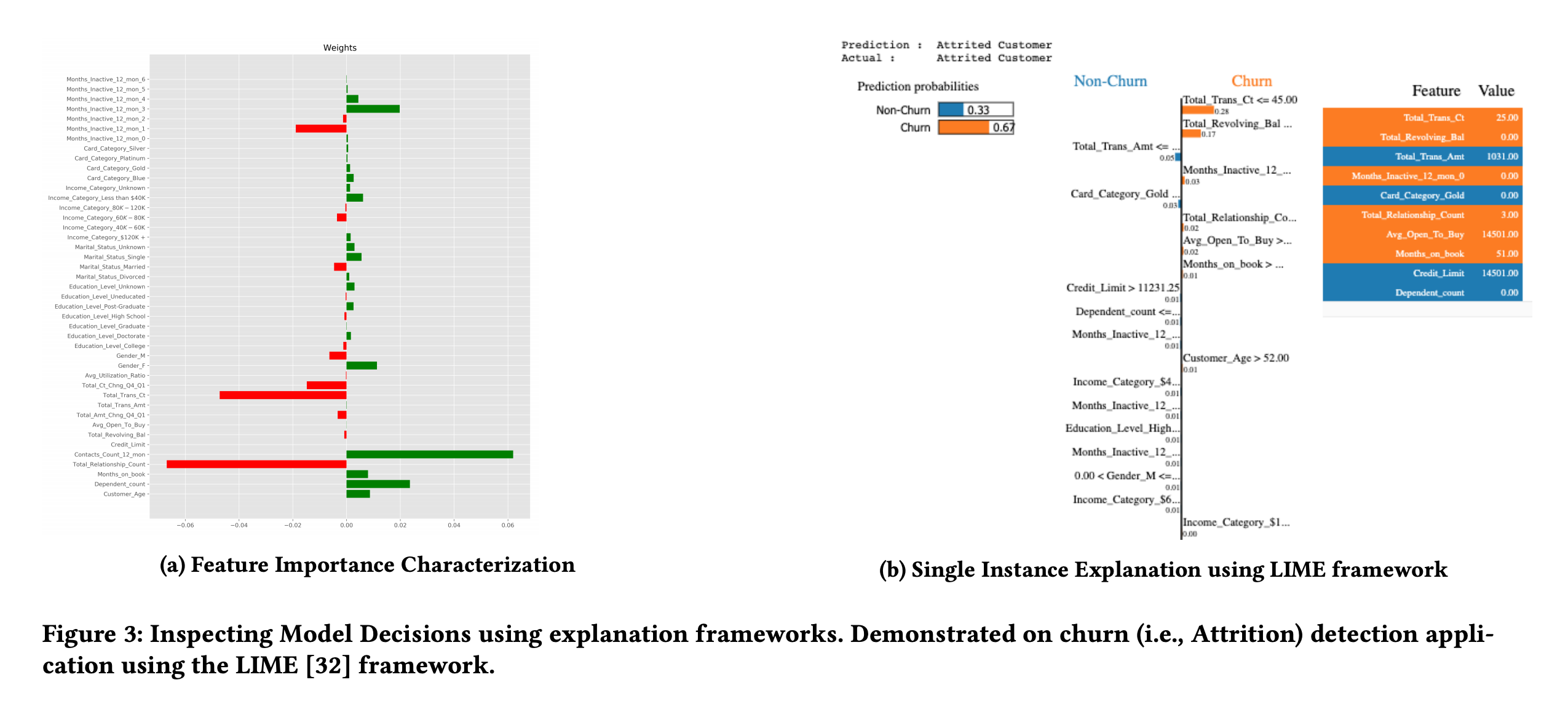
이러한 문제들에 대처하기 위해서는 배포된 모델에 대한 monitoring, track, debug가 가능해야 합니다. 논문에서는 이를 위해 Meta-model을 제안합니다. Meta-model 이란 배포된 모델의 모든 예측값을 평가하고 신뢰할 수 있는지 판단하는 모델을 뜻 합니다. 논문에서는 Meta-model을 사용하는 2가지 방법을 제시합니다.
- Performing duplicate detection, filling in missing values, and is also used to fine-tune precision / recall by suppressing alerts deemed to be of low quality.
- Inspect model decisions further by employing explanation frameworks like LIME.
3. Tuning-under-the-Carpet AntiPattern
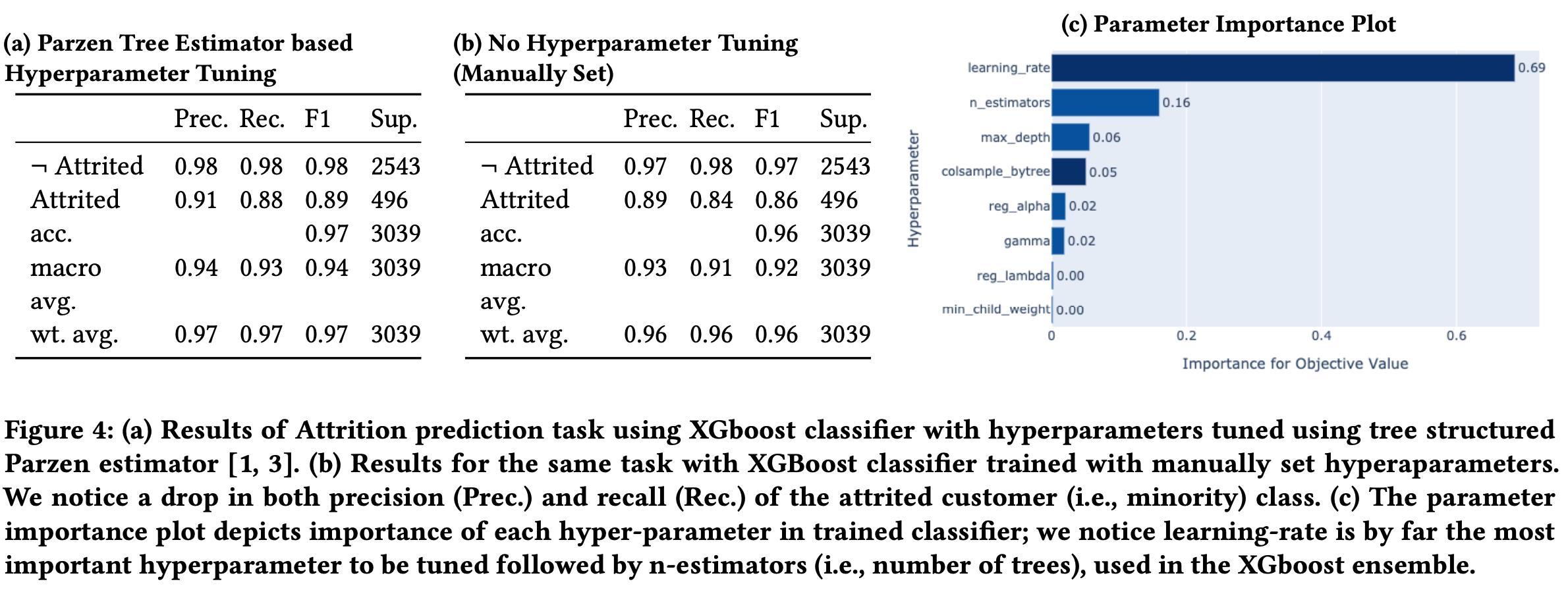
머신러닝과 딥러닝을 학습할 때 가장 중요한 부분은 바로 hyper-parameter 입니다. Baseline 모델과 hyper-parameter tuning이 된 모델의 성능 차이는 크다고 여러 연구에서 증명되었습니다. 배포하는 모델의 성능을 높이려면 이러한 hyper-parameter tuning을 쉽게 이용할 수 있어야 합니다. 또한 재현이 가능해야 합니다.
4. ‘PEST’ AntiPattern
실제로 성능이 검증되지 않는 기법이 파이프라인에 바로 적용되는 상황입니다.
지금도 많은 학회에서 모델의 성능을 높이기 위한 여러 기법들이 발표되고 있습니다. 그런데 연구 환경과 실제 환경의 차이로 인해서 새로운 기법이 현재 배포되고 있는 모델에서는 같은 효과를 보이지 않는 경우도 많습니다. 그래서 실제 데이터에 검증되지 않은 새로운 기법을 바로 적용할 수 없습니다.
이러한 새로운 기법을 실험을 실제 모델과 동일한 파이프라인에서 진행할 수 있어야 합니다.
5. Bad Credit Assignment AntiPattern
모델 성능 향상의 요인을 정확히 파악할 수 없는 상황입니다.
머신러닝 파이프라인에서 모델의 성능이 향상되는 부분은 각 과정마다 일어날 수 있습니다. 논문에서는 다음과 같은 과정들을 제시합니다.
- A function of clever problem formulations
- Data preprocessing
- Hyperparameter tuning
- application of existing well-established methods to interesting new tasks as detailed by paper.
정확한 성능 향상의 요인을 알기 위해서는 수정이 되는 부분을 제외하고 다른 부분은 계속해서 동일한 환경에서 실험이 이루어져야 합니다.
6. Grade-your-own-Exam AntiPattern
Test 데이터가 독립적이지 못한 상황입니다. 일반적으로 머신러닝 실험을 할 경우 평가와 test 데이터가 독립적으로 샘플링되어야 합니다. 또한 test 데이터는 최종적인 모델 평가 전에는 사용되어서는 안됩니다. 만약 test 데이터가 모델을 평가할 때 계속 사용된다면 HARKing (Hypothesizing After Results are Known)에 빠지게 됩니다. HARKing이란 모델을 만드는 사람이 성능을 test 데이터에 대해서 확인하고 모델의 성능을 올리는 과정을 뜻합니다. 이 과정은 잠재적인 data leakage를 야기하게 됩니다.
이를 위해서 모델링을 담당하는 팀은 독립적인 ‘‘Ground Truth system’을 구성해서 API를 통해 예측 데이터를 얻어와 예측을 할 수 있어야 합니다.
7. Set&Forget AntiPattern
Concept drift에 대응할 수 없는 상황입니다. 일반적으로 머신러닝 파이프라인을 만들 때 데이터 샘플링이 i.i.d 한 상황에서 이루어진다고 가정합니다. 그래서 한번 모델 학습과 예측을 설정하고 나면 잊어 버리는 경우(Set & Forget)가 많습니다. 그런데 실제 상황에서는 예측해야 하는 값의 통계적 특성이 변화하는 경우(Concept Drift)가 발생합니다.
In predictive analytics and machine learning, concept drift means that the statistical properties of the target variable, which the model is trying to predict, change over time in unforeseen ways. This causes problems because the predictions become less accurate as time passes.
출처: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Concept_drift
이러한 concept drift에 대처하기 위해서는 의사결정을 도와주는 보조 시스템(Decision support system)이 필요합니다. Concept drift를 대처하기 위해 의사결정나무와 같은 해석이 가능한 tree-based 를 이용할 수 있습니다.
자세한 방법은 논문에서 인용한 논문을 참고하시기 바랍니다.
8.‘Communicate with Ambivalence’ AntiPattern
잘 보정되지 않은 모델을 배포함으로서 머신러닝 파이프라인 전체의 신뢰도 하락이 일어나는 상황입니다. 잘 보정된 모델은 Brier score가 잘 보정 되었다는 뜻입니다.
만약 보정되지 않는 모델을 사용한다면 파이프라인의 어디가 문제인지 정확히 진단할 수 없게 됩니다. 그래서 최근 연구에서는 모델의 설명 가능성 뿐만 아니라 모델의 불확실성을 전달하는 것도 중요하다고 합니다.
- Brier Score란?
The Brier Score is a strictly proper score function or strictly proper scoring rule that measures the accuracy of probabilistic predictions. For uni dimensional predictions, it is strictly equivalent to the mean squared error as applied to predicted probabilities.
출처: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brier_score
Brier Score 수식은 다음과 같습니다.
$$BS=\frac{1}{N}\sum_{t=1}^N (f_{t}-o_{t})^2$$
- $N$: the number of items you’re calculating a Brier score for
- $f_{t}$: is the forecast probability (i.e. 25% chance)
- $o_{t}$: is the outcome (1 if it happened, 0 if it didn’t)
출처: https://www.statisticshowto.com/brier-score/
Brier Score가 0에 가까울 수록 모델이 잘 보정되었다고 해석할 수 있습니다.
9.‘Data Crisis as a Service’ AntiPattern
모델을 개발하는 과정에서 데이터가 수정되는 과정이 기록되지 않는 상황입니다. 이 과정이 반복된다면 모델 학습에 사용한 데이터가 어떤 과정을 거쳤는지 확인할 수 없게 됩니다.